前言 对于分布式系统,内部组件众多,而组件之间的联系就需要一套非常高效的通信机制,Flink底层的RPC框架是基于Akka实现。 本文着重通过一些例子来分析flink底层的通信机制
文章结构 文章结构如下:
Akka介绍与简单例子
Flink RPC实例以及Rpc通信底层源码分析
调用远程的RPC流程
总结
Akka介绍与简单例子 Akka 是什么
一个开发并发、容错、可伸缩应用的框架
构建在JVM至上,基于Actor模型
定义一组规则,规定一组系统中每个模块之间如何交互,如何回应。
Actor 解决什么问题 开发高效率的并发程序,充分利用CPU资源。解决传统多线程方法的维护困难和容易发生错误的问题。对并发模型有一个更好的抽象。异步非阻塞。
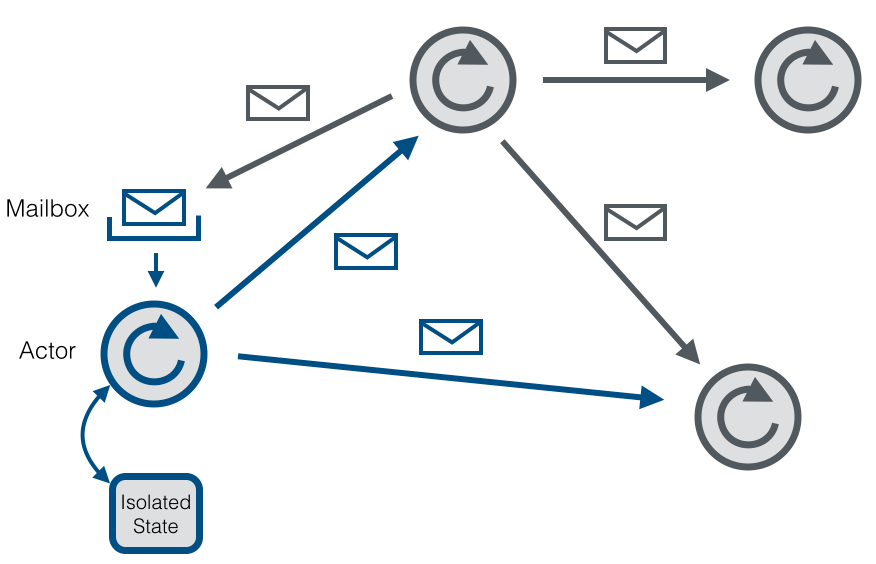
Akka模型组成原理 下面是一张来自官网的图片,形象的介绍了Actor的内部模型。
Actor是最小的单元模块,系统有n个Actor组成,每个Actor有由mailbox和自身状态组成。
Actor和Actor是通过信件进行通信,每个Actor是串行处理每一条消息的。并且信件是不可变的。
例子 Akka的创建和执行流程
构建ActorSystem
创建Actor
不能直接New一个Actor,而是你用通过actorSystem的actorOf方法创建,并且返回的是Actor的引用ActorRef,通过引用操作Actor
发送消息
回应消息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 public class AkkaTest { private static ActorSystem actorSystem = null ; private ActorRef helloActor = null ; private ActorRef hiActor = null ; @BeforeClass public static void setup () { actorSystem = AkkaUtils.createDefaultActorSystem(); } @Before public void init () { helloActor = actorSystem.actorOf(Props.create(HellowActor.class), "helloActor" ); hiActor = actorSystem.actorOf(Props.create(HiActor.class), "hiActor" ); } @AfterClass public static void teardown () throws Exception { actorSystem.terminate(); } @Test public void testSay () { helloActor.tell("jack" , hiActor); } public static class HellowActor extends AbstractActor { @Override public Receive createReceive () { return ReceiveBuilder.create() .matchAny(this ::handleMessage) .build(); } private void handleMessage (Object message) { System.out.println("hello!" + message); getSender().tell("mary" , this .getSelf()); } } public static class HiActor extends AbstractActor { @Override public Receive createReceive () { return ReceiveBuilder.create() .matchAny(this ::handleMessage) .build(); } private void handleMessage (Object message) { System.out.println("hi! " + message); } } }
运行结果
Flink RPC实例分析 话不多说,直接上代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class RpcEndpointTest extends TestLogger { private static final Time TIMEOUT = Time.seconds(10L ); private static ActorSystem actorSystem = null ; private static RpcService rpcService = null ; @BeforeClass public static void setup () { actorSystem = AkkaUtils.createDefaultActorSystem(); rpcService = new AkkaRpcService (actorSystem, AkkaRpcServiceConfiguration.defaultConfiguration()); } @AfterClass public static void teardown () throws Exception { final CompletableFuture<Void> rpcTerminationFuture = rpcService.stopService(); final CompletableFuture<Terminated> actorSystemTerminationFuture = FutureUtils.toJava(actorSystem.terminate()); FutureUtils .waitForAll(Arrays.asList(rpcTerminationFuture, actorSystemTerminationFuture)) .get(TIMEOUT.toMilliseconds(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } @Test public void testSelfGateway () throws Exception { int expectedValue = 1337 ; BaseEndpoint baseEndpoint = new BaseEndpoint (rpcService, expectedValue); try { baseEndpoint.start(); BaseGateway baseGateway = baseEndpoint.getSelfGateway(BaseGateway.class); CompletableFuture<Integer> foobar = baseGateway.foobar(); assertEquals(Integer.valueOf(expectedValue), foobar.get()); } finally { RpcUtils.terminateRpcEndpoint(baseEndpoint, TIMEOUT); } } public static class BaseEndpoint extends RpcEndpoint implements BaseGateway { private final int foobarValue; protected BaseEndpoint (RpcService rpcService, int foobarValue) { super (rpcService); this .foobarValue = foobarValue; } @Override public CompletableFuture<Integer> foobar () { return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(foobarValue); } } public interface BaseGateway extends RpcGateway { CompletableFuture<Integer> foobar () ; } }
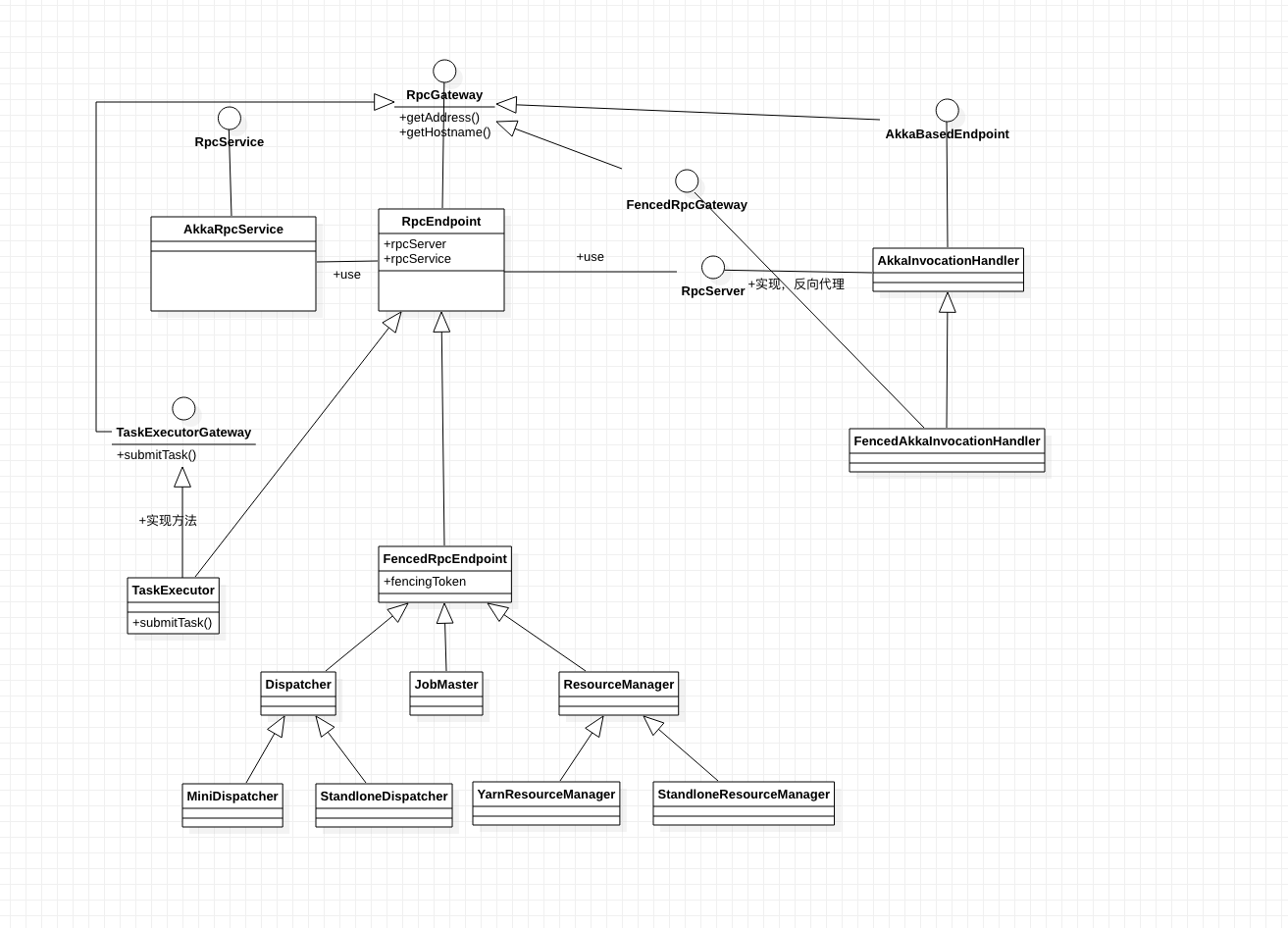
上面出现了几个比较重要的类或者接口,具体类图如下,下面一个个来介绍
RpcGateway 有两个方法,getAddress和getHostname,首先想想,RPC,全程为远程过程调用,要想调用另外一个进程的过程,则需要知道这个过程的地址和端口,这个相当于是一个代理,或者说是一个网关,一个端点或者说进程想要被远程调用,则必须实现这个方法,并且一般由一个接口来继承RpcGateway,并且在这个接口中定义一些方法,然后在实现类中实现这些方法给远程调用。 而在RPC的客户端,则返回的是这个gateway。 基本所有的组件都继承了这个RpcGateway或者他的子接口。
RpcServer 和 AkkaInvocationHandler 比较难理解的就是这两个类,第一个接口,可以把它理解成一个和远端交互的能力,这个接口也实现了RpcGateway。
AkkaInvocationHandler是RpcServer的一个Akka实现,同时实现了InvocationHandler,表明也是一个代理调用处理器,他是由RpcService在一个endpoint启动的时候创建。
RpcEndpoint 这个类是和Actor绑定的,每个RpcEndpoint都有一个Actor对应,并且实现了RpcGateway接口对于同一个Endpoint,所有的调用都运行在主线程,因此不会有并发问题 ,当启动RpcEndpoint/进行Rpc调用时,其会委托RcpServer进行处理。
RpcService 这个类相当于一个服务工具类,主要起到根据Endpoint来启动 RpcServer(Actor),连接到某一个RpcServer,并且返回一个RpcGateway,停止服务等
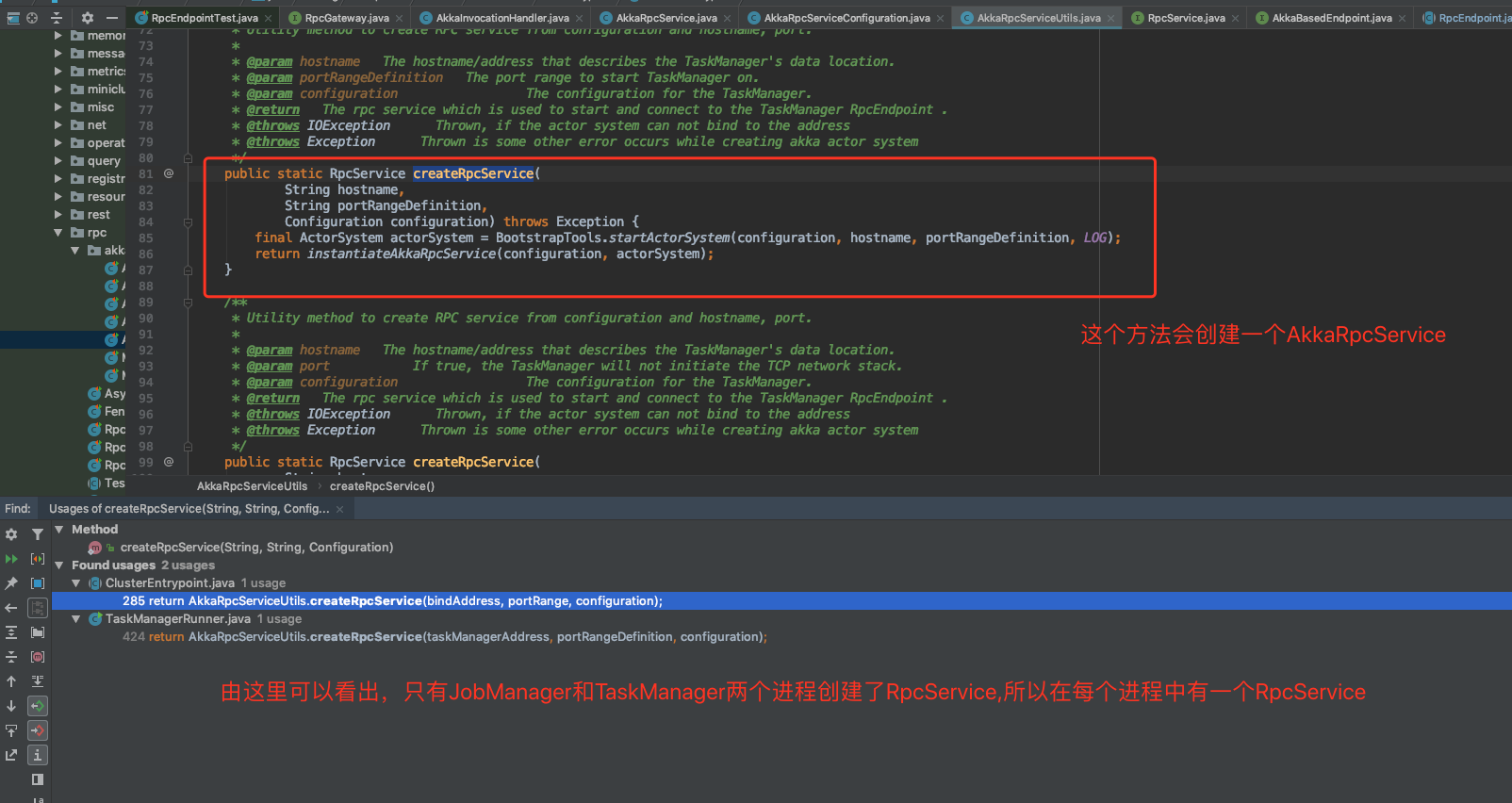
AkkaRpcService RpcService的实现类,也就是Akka的实现。封装了ActorSystem,RPC服务启动一个Akka参与者来接收来自RpcGateway}的RPC调用
请看下图和其中的解释。
在这个类中有一个Map 声明如下,他保存了每一个ActorRef和RpcEndpoint的映射关系,作用是在停止服务的时候停止actor
1 private final Map<ActorRef, RpcEndpoint> actors = new HashMap <>(4 );
RPCEndPoint初始化过程 下面来看看具体一个RpcEndpoint实例化的源码解析
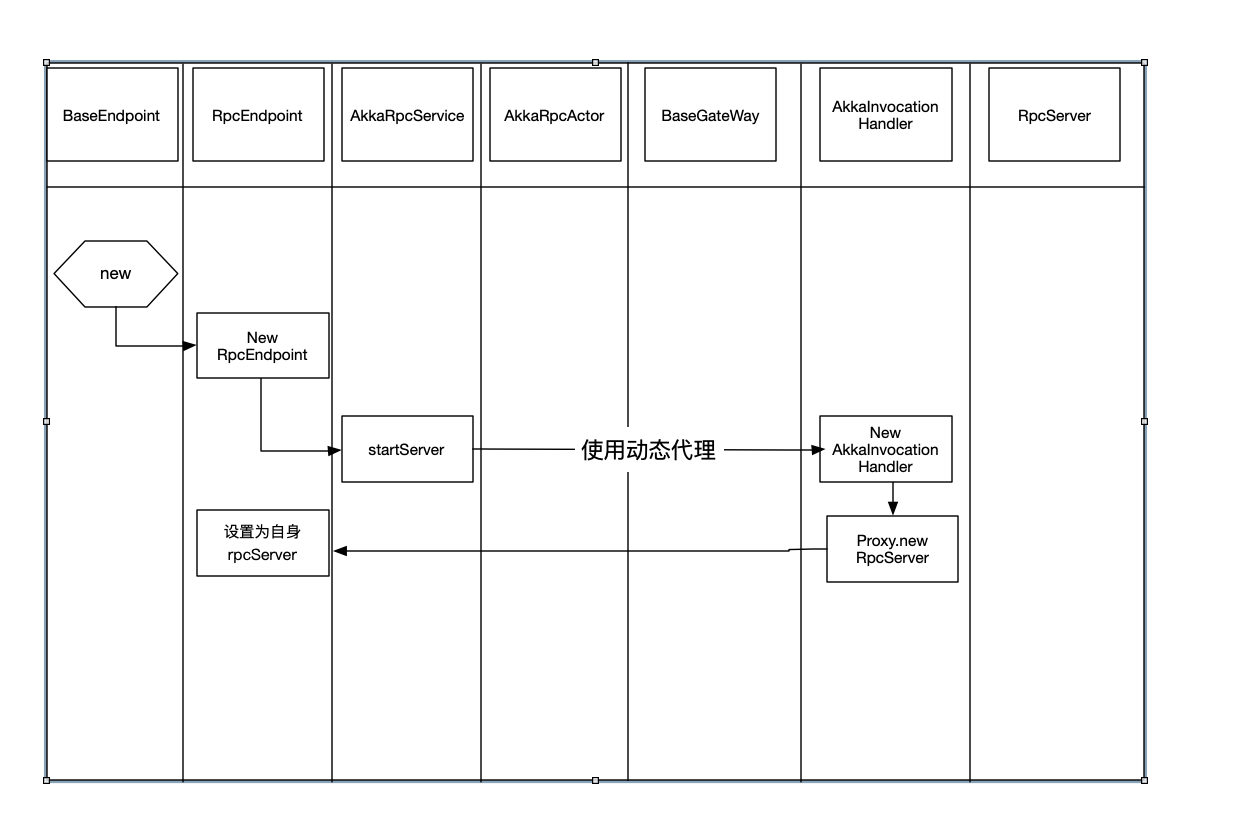
在实例化RpcEndpoint的时候,进入到构造函数中,传入了上面实例化的RpcService还有endpointId,每个endpoint都有一个唯一的endpointid,在构造函数中做了两件事:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 protected RpcEndpoint (final RpcService rpcService, final String endpointId) { this .rpcService = checkNotNull(rpcService, "rpcService" ); this .endpointId = checkNotNull(endpointId, "endpointId" ); this .rpcServer = rpcService.startServer(this ); this .mainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor (rpcServer, this ::validateRunsInMainThread); }
启动rpcSerer,并且将返回的rpcServer赋值到类变量rpcServer上,注意,这里返回的rpcServer,是一个代理类,在调用rpcServer的时候,会被invoke方法拦截。
设置 this.mainThreadExecutor =MainThreadExecutor(rpcServer, this::validateRunsInMainThread),首先这个类的构造函数有一个参数为MainThreadExecutable gateway,RpcServer继承了此接口,而AkkaInvocationHandler实现了RpcServer,则也实现了这个接口,MainThreadExecutable接口中有 runAsync、callAsync、scheduleRunAsync等方法,标识在底层RPC端点的主线程中执行runnable。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 protected static class MainThreadExecutor implements ComponentMainThreadExecutor { private final MainThreadExecutable gateway; private final Runnable mainThreadCheck; MainThreadExecutor(MainThreadExecutable gateway, Runnable mainThreadCheck) { this .gateway = Preconditions.checkNotNull(gateway); this .mainThreadCheck = Preconditions.checkNotNull(mainThreadCheck); } public void runAsync (Runnable runnable) { gateway.runAsync(runnable); } public void scheduleRunAsync (Runnable runnable, long delayMillis) { gateway.scheduleRunAsync(runnable, delayMillis); } public void execute (@Nonnull Runnable command) { runAsync(command); } ...
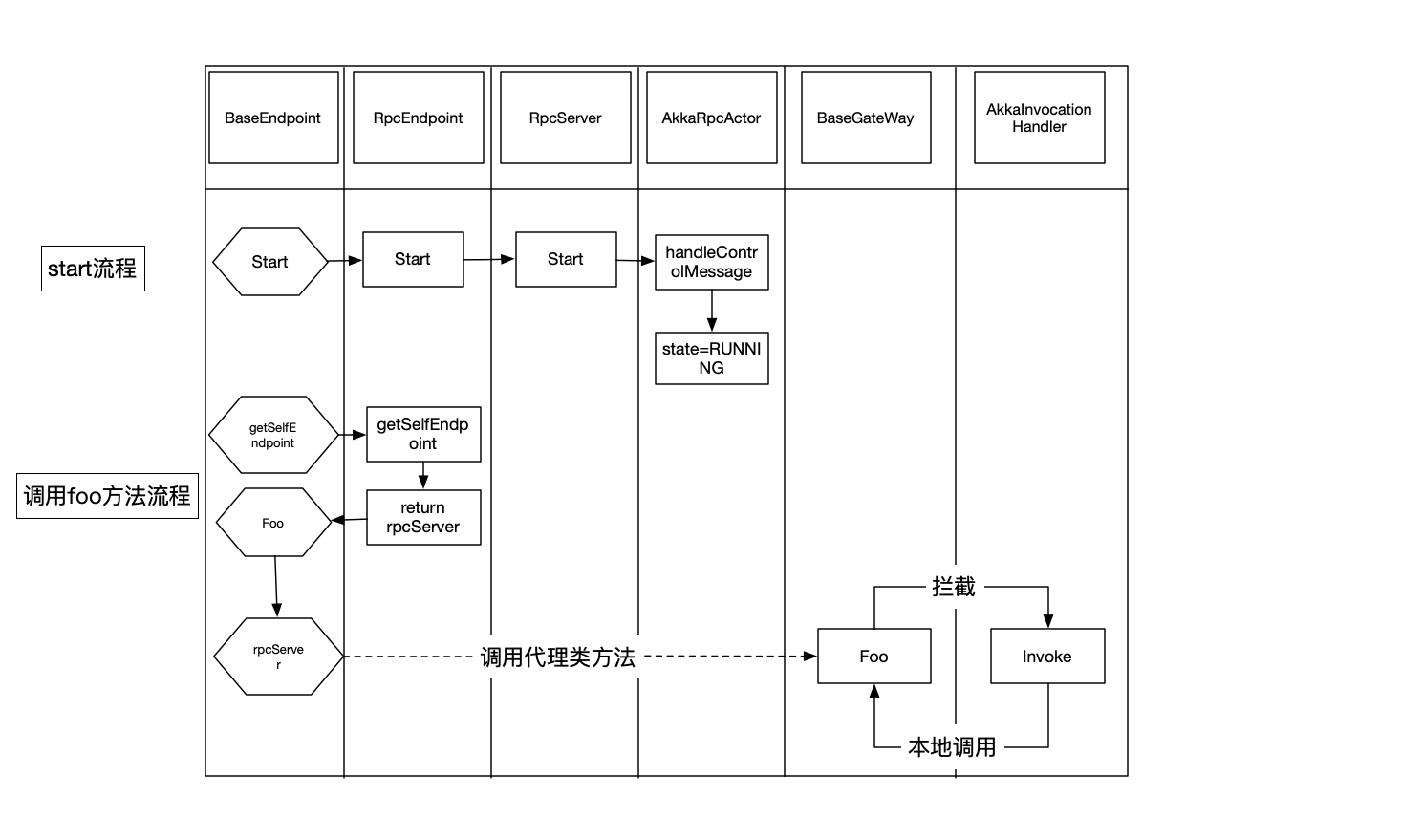
RpcEndpoint通信过程 当初始化完成之后,就可以发送消息,请看图。
start流程 上面实例化RpcEndpoint后,当中的rpcServer的状态Stop的,需要调用start方法
调用RpcEndpoint#start
转发给本身的RpcServer#start
因为这个rpcServer是一个代理类,所以转发到了AkkaInvocationHandler中去了,被拦截了
这里首先是获取这个方法的定义方法,如果是在AkkaBasedEndpoint、Object、RpcGateway、StartStoppable、MainThreadExecutable、RpcServer中调用的呢,代表是本地调用,或者说是初始化调用,肯定是不涉及到远程的,则直接调用响应方法就可以了
这里传入的对象是自己本身。
调用AkkaInvocationHandler#start;
通过ActorRef#tell给对应的Actor发送消息rpcEndpoint.tell(ControlMessages.START, ActorRef.noSender());;
调用AkkaRpcActor#handleControlMessage处理控制类型消息;
在主线程中将自身状态变更为Started状态;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); Object result; if (declaringClass.equals(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class) || declaringClass.equals(Object.class) || declaringClass.equals(RpcGateway.class) || declaringClass.equals(StartStoppable.class) || declaringClass.equals(MainThreadExecutable.class) || declaringClass.equals(RpcServer.class)) { result = method.invoke(this , args); } else if (declaringClass.equals(FencedRpcGateway.class)) { ... } else { result = invokeRpc(method, args); } return result; }
调用远程的RPC流程 要实现远程调用,主要通过 AkkaRpcService的connect方法实现,连个参数,一个address,一个clazz,这个clazz是这个方法要返回的代理类的接口类型,比如DispatcherGateway ,他定义了很多方法。
AkkaRpcService.java#connect
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override public <C extends RpcGateway > CompletableFuture<C> connect ( final String address, final Class<C> clazz) { return connectInternal( address, clazz, (ActorRef actorRef) -> { Tuple2<String, String> addressHostname = extractAddressHostname(actorRef); return new AkkaInvocationHandler ( addressHostname.f0, addressHostname.f1, actorRef, configuration.getTimeout(), configuration.getMaximumFramesize(), null ); }); }
然后继续往下走,定义了connectInternal方法,,请看注释
AkkaRpcService.java#connectInternal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 private <C extends RpcGateway > CompletableFuture<C> connectInternal ( final String address, final Class<C> clazz, Function<ActorRef, InvocationHandler> invocationHandlerFactory) { checkState(!stopped, "RpcService is stopped" ); LOG.debug("Try to connect to remote RPC endpoint with address {}. Returning a {} gateway." , address, clazz.getName()); final ActorSelection actorSel = actorSystem.actorSelection(address); final Future<ActorIdentity> identify = Patterns .ask(actorSel, new Identify (42 ), configuration.getTimeout().toMilliseconds()) .<ActorIdentity>mapTo(ClassTag$.MODULE$.<ActorIdentity>apply(ActorIdentity.class)); final CompletableFuture<ActorIdentity> identifyFuture = FutureUtils.toJava(identify); final CompletableFuture<ActorRef> actorRefFuture = identifyFuture.thenApply( (ActorIdentity actorIdentity) -> { if (actorIdentity.getRef() == null ) { throw new CompletionException (new RpcConnectionException ("Could not connect to rpc endpoint under address " + address + '.' )); } else { return actorIdentity.getRef(); } }); final CompletableFuture<HandshakeSuccessMessage> handshakeFuture = actorRefFuture.thenCompose( (ActorRef actorRef) -> FutureUtils.toJava( Patterns .ask(actorRef, new RemoteHandshakeMessage (clazz, getVersion()), configuration.getTimeout().toMilliseconds()) .<HandshakeSuccessMessage>mapTo(ClassTag$.MODULE$.<HandshakeSuccessMessage>apply(HandshakeSuccessMessage.class)))); return actorRefFuture.thenCombineAsync( handshakeFuture, (ActorRef actorRef, HandshakeSuccessMessage ignored) -> { InvocationHandler invocationHandler = invocationHandlerFactory.apply(actorRef); ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") C proxy = (C) Proxy.newProxyInstance( classLoader, new Class <?>[]{clazz}, invocationHandler); return proxy; }, actorSystem.dispatcher()); }
AkkaRpcActor.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private void handleHandshakeMessage (RemoteHandshakeMessage handshakeMessage) { if (!isCompatibleVersion(handshakeMessage.getVersion())) { sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaHandshakeException ( String.format( "Version mismatch between source (%s) and target (%s) rpc component. Please verify that all components have the same version." , handshakeMessage.getVersion(), getVersion()))); } else if (!isGatewaySupported(handshakeMessage.getRpcGateway())) { sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaHandshakeException ( String.format( "The rpc endpoint does not support the gateway %s." , handshakeMessage.getRpcGateway().getSimpleName()))); } else { getSender().tell(new Status .Success(HandshakeSuccessMessage.INSTANCE), getSelf()); } }
总结 主要介绍了rpc通信的核心类,以及Actor初始化流程和远程调用的流程。
好类,总算讲了个大概,flink源码博大精深,有很多地方值得我们学习的,鄙人才疏学浅,可能有疏漏之处,也可能有些地方讲的不对,请多指教。